
Oct 20, 2022
Blog Life Sciences The Advantages and Disadvantages of Insulin Drug and Delivery Technologies
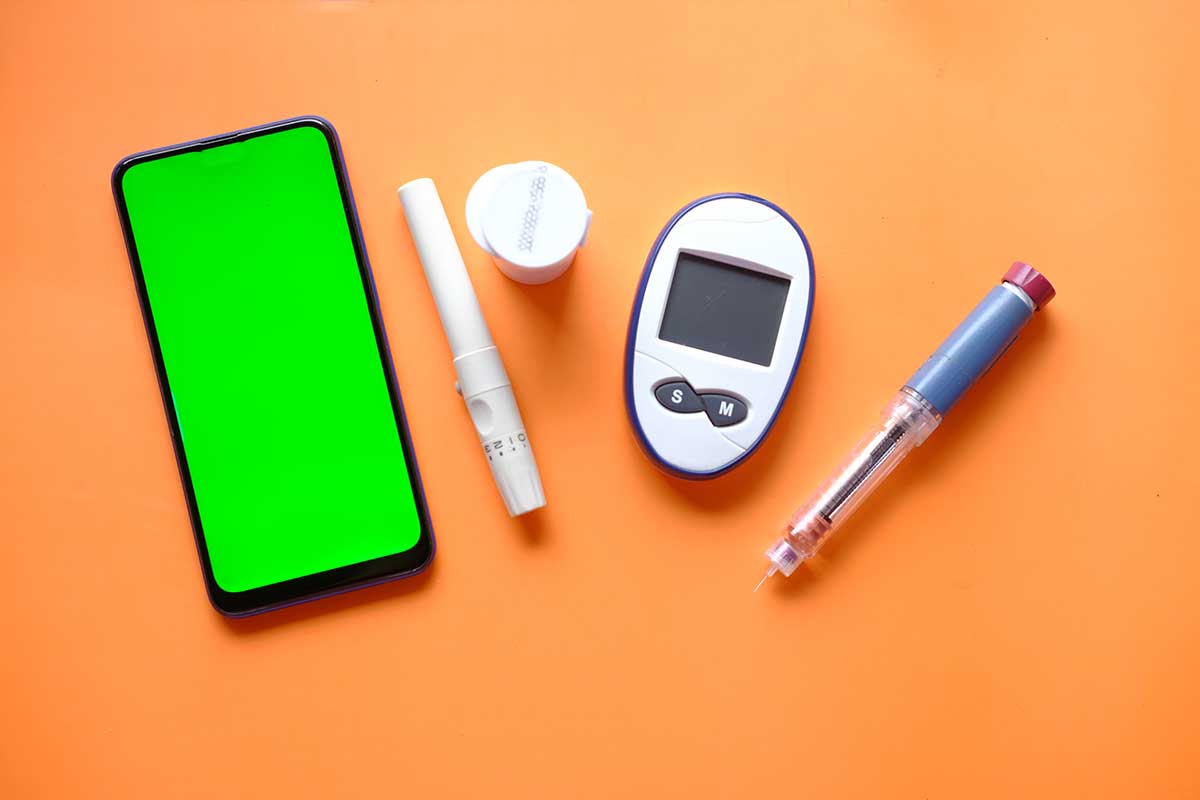
With the advancement of technology within the drug delivery systems industry, insulin delivery systems have rapidly evolved to suit the user in terms of convenience and ease of use. BCC analysts predict that the market growth is attributed to factors such as the increasing incidence of diabetes and novel insulin drug and delivery technologies.
Insulin delivery systems are categorized into four sections by BCC Research: syringes, insulin pens, insulin pumps, and smart pens. Insulin delivery systems are vital in the daily management and care of patients with diabetes. In our latest report on insulin drug and delivery technologies, our analysts determine that traditional syringes and insulin pumps are being replaced by reusable and disposable insulin pens due to the latter’s portability, greater dosage accuracy, and ease of use.
With the healthcare industry and its care providers already working overtime to provide the best quality of care for patients, the introduction of technology that allows patients to gain autonomy over the management of their disease is a welcome introduction by all. As with most chronic diseases, patients don’t always fall under a one size fits all approach in terms of their treatment. Through research and developments in insulin technology, patients can administer insulin as and when the time is suitable or necessary for themselves in line with their individual health plan.
Conventional technologies as well as advanced technologies exist within the market. Each technology is suited to the different needs and economic situations of the patient.
The administration of multiple daily injections of long-acting basal insulin and rapid-acting prandial insulin formulations is the most recommended intensive insulin therapy regimen for type one diabetics. The global market for drug and delivery devices by type reveals that syringes will reach $36,957.2 million by 2027 at a CAGR of 8.7% situating itself way ahead of the other devices. Syringes serve as the standard for intensive type one diabetes management; however, this is not to say it is without its grievances.
The number of insulin injections required exceeds three per day, which is timely and inconvenient for patients. Research suggests it may negatively impact good glycemic control. The main advantages and disadvantages of syringes as an insulin delivery technology are:
Advantages
Disadvantages
An insulin pen differs from a syringe in that it is an injection device that is around the shape and size of a large marker pen. It helps to deliver insulin into the fatty tissue via a short, thin disposable needle. Frequently used by travelers, insulin pens integrate the medication and delivery system, making them more convenient than syringes. The user simply twists or snaps on a new needle, dials a dose, injects the insulin, and discards the used needle into a needle-safe container.
Advantages
Disadvantages
Invented in the 1980s, insulin pumps are a step away from traditional manual devices. The insulin pump is a complex battery-operated, computerized electronic device that can be programmed to provide continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. The insulin pump is programmed and can be customized to meet individual needs. It delivers rapid-acting insulin to the patient continuously to ensure basal blood insulin levels. Immediately before eating, the patient manually programs the pump to deliver a larger supplemental dose (bolus dose) of rapid-acting insulin. Although convenient, insulin pumps come with inherent limitations, including the increased likelihood of diabetic ketoacidosis, irritation, and scarring of the insertion site. The future of insulin pump therapy is promising, as it is an excellent alternative to conventional injections for type one diabetes patients of all ages.
Advantages
Disadvantages
Smart pens show great promise for diabetes management. Smartpen technology records the amount and timing of each insulin dose and wirelessly transmits the information to a dedicated mobile application. It also offers dosing recommendations and prepares reports for healthcare professionals. Within the global market for insulin delivery technology smart pens deliver the highest compound annual growth rate over the forecast period at 12.6%, expected to reach $7,666.6 million by 2027 from $3,554.1 million in 2022.
Smart insulin pens are relatively new to the insulin delivery device game so clear advantages and disadvantages aren’t as researched as others. However, the gap in the market for an insulin device which reflects the current relationship between healthcare and technology is being cornered by the introduction of these devices. These evolved insulin pens gained digital displays and memory of the most recent doses. Smart pens are designed to be simple to use. Once you’ve downloaded the app to your smartphone and paired it with your pen, you’re ready to go. The device sends real-time data to the app via Bluetooth connection, defining smart pens as the future of insulin delivery device technologies.
The tides are changing within the insulin delivery industry, and smarter technologies are slowly gaining momentum through the market chain. In a society in which wearable technology can monitor your heart and track health conditions, patients have an increased awareness of self-care which reflects the growing popularity of smart insulin drug delivery technology that provides basic health data in a user-friendly format.
The global market for insulin drug and delivery technologies is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.8% to reach over $88.9 billion by the end of 2027. BCC analysts predict a strong future for insulin drug delivery systems in the adoption and development of smart devices, as discussed in our latest report: Global Markets for Insulin Drug and Delivery Technologies.
Download your complimentary report overview or purchase the single report.
Alternatively, become a BCC member today and gain access to portfolios of industry-specific reports.

Katie Biddle joined BCC Research as a junior copywriter in 2022 and works within the marketing team. Prior to BCC, she recently graduated with a BA in Creative Writing and English Literature from Westminster University.
In today’s fast-paced biomedical world, researchers and pharmaceutical companies...
Radiopharmaceuticals represent a cutting-edge frontier in modern medicine, offer...

Implantable Remote Patient Monitoring (IRPM) devices are revolutionizing healthc...

We are your trusted research partner, providing actionable insights and custom consulting across life sciences, advanced materials, and technology. Allow BCC Research to nurture your smartest business decisions today, tomorrow, and beyond.
Contact UsBCC Research provides objective, unbiased measurement and assessment of market opportunities with detailed market research reports. Our experienced industry analysts assess growth opportunities, market sizing, technologies, applications, supply chains and companies with the singular goal of helping you make informed business decisions, free of noise and hype.